
Tuesday, February 26, 2008
Mitosis

Monday, February 25, 2008
The Cell Cycle.
- To make new cells
- Continuity of life: Asexual reproduction, growth, repair, and renewal
- Cell cycle: Make a copy of a preexisting cell (Daughter cells)
What's in a cell that smells so sweet.......ehhh
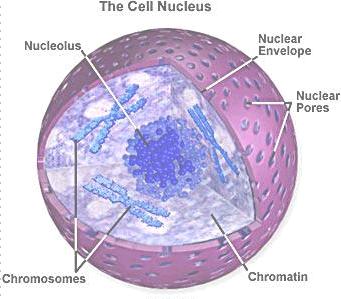

- Nucleus: Chromosomes, DNA
- Cytoskeleton: "Scaffolding" or "Skeleton"; The internal framework of a cell, composed largely of actin filaments and microtubules (spindle fibers). Also includes Centrioles (in animaks).
The Nucleus:
Its function: to protect DNA
Centrioles:
One of two cylindrical cellular structures that are composed of nine triplet microtubules and form the asters during mitosis.
Centrioles are involved in the organization of the mitotic spindle and in the completion of cytokinesis.
Centrioles are an important part of centrosomes, which are involved in organizing microtubules in the cytoplasm.
They organize spindle fibers and guide chromosmes in mitosis.
Daughter Cells:
During mitosis, an exact copy of DNA is made from the parent cell to be passed to the daughter cells.
Cytokinesis: division of orgnanelles and cytoplasm
Mitosis:
Interphase: Defined only by the absence of cell division. During interphase, the cell obtains nutrients, and duplicates its chromatids. Most eukaryotic cells spend approximately 90% of its life in Interphase. "Every day job": produces RNA, synthesize proteins and enzymes, prepares for duplication if triggered.
Prophase: Stage during which the chromosomes condense and become visible, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the spindle apparatus forms at opposite poles of the cell.
Pro-Metaphase: The stage of mitosis or meiosis in which the nuclear membrane disintegrates, the centrioles reach the poles of the cell, and the chromosomes continue to contract.
Metaphase: Condensed chromosomes align in the middle of the cell before being separated into each of the two daughter cells.
Anaphase: The chromosomes move from the equatorial plate toward opposite ends of the nuclear spindle.
Telophase: The chromosomes of daughter cells are grouped in new nuclei.
Cytokinesis: The division of the cytoplasm of a cell following the division of the nucleus.
Cell Life Cycle:
Interphase:
Divided into three phases:
-G1: first gap
Cell doing everyday job
Cell grows
-S: DNA Synthesis: Copies chromosomes
-G2: second gap
Prepares for division
Cell grows more
Produces organelles, proteins, and membranes
FIN
Oh tomorrows sherpa is...............Maria
Friday, February 22, 2008
Science Debate 2008
http://sciencedebate2008.com
Would be great if you students got to see this.
==========================================
Universities, corporations and a host of individuals are calling for a debate with all four of the remaining presidential candidates discussing critical scientific issues that impact everything from the environment to the economy.
Sciencedebate2008.com, formed by two Hollywood screenwriters who had time to mull science recently while on strike, is an effort aimed at thrusting technology into the limelight.
One of the initiative's founders, Shawn Otto, said yesterday more than 17,000 American universities and the editors of nearly every major science publication in the nation have added their names to the Web site, encouraging the presidential hopefuls to debate key scientific issues.
"This is a nonprofit organization we set up to raise the profile of science and technology in our national political diaglogue," Otto said, adding that his initiative is now being co-sponsored by the National Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Medicine, the National Academy of Engineering, the Council on Competitiveness and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Yesterday, John Podesta, chief of staff for former President Bill Clinton, posted a video statement on YouTube echoing that science remains one of the nation's primary areas of focus. He called for a presidential debate "in charting a path forward on national security, on energy and climate change policy, really on the core fundamentals of our economic policy."
Otto said it would be "really fabulous" to see Democrats and Republicans on the same stage debating issues in science.
"All of us believe that almost every major policy challenge that the next president will face revolves around questions of science and technology," Otto said, referring to signers of his initiative.
"Ever since World War II, America has been leading in science and technology, and science and engineering have driven half of our economic growth."
But in the not-too-distant future, he added, 90 percent of all scientists will be living in Asia, causing a major "shift in intellectual capital."
John Porter on Science Debate 2008
Francesca Grifo on Science Debate 2008
Monday, February 11, 2008
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: HORMONES
- metabolism
- growth
- development
- maturation
- reproduction

There are 2 major types of hormones:
- Protein-based Hormones
These hormones are made of proteins including polypeptides suc as insulin and ADH (anti diuretic hormone). Glycoproteins are toher protein hormones that have proteins and carbohydrates. These include FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) and LH( luteinizing hormone). Amines are another type which are modified by amino acids like epinephrine and melatonin. Protein based hormones are hydrophillic and are not lipid soluble. That means they can't diffuse across a membrane. The protein hormone has to bind to receptors on top of the plasma membrane that are embedded in the membrane. The homrone fits into the protein in the membrane and causes a conformational change. The protein that receives the hormone stimulus changes chape which causes another protein at the other end to carry the message along. This secondary messenger pathway is triggered. Enzyme action, uptake or secretion of molecules is activated. 2. Lipid-based Hormone
These hormone include steroids which are modifed cholesterol such as sex hormones and aldosterone. Lipid based hormones are hydrophobic which means they are lipid soluble. They can diffuse right through the cell membrane without being stopped at the cell membrane and having to go through a receptor on the membrane. These hormones bind to receptor proteins in the cytoplasm and some on the nucleus. Lipid hormones bind to DNA as transcription factors. The hormone causes a conformational change. The transcription factor is the protein on the DNa that coordinates which genes should be transcripted onto the mRNA to make a protein. Lipid hormones are carried on a protein carrier because they are not soluble in water since oil and water don't mix. The hormone can cause a major long term change in the body such as growth. The growth factors can affect hair, bone, muscle and gametes.


Oh Yeah Tuesday night's sherpa will be Shannah.
Sunday, February 10, 2008
Well, well, here it is--the missin' blogs: B CELLS (2/6) & T CELLS (2/8)
Well first and formost i would like to appologize to my fellow class mates as i always do for not having the sherpa repost in on Time.... ma bad. Well the library is a quiet place to work so i guess this is where i'll be writtin from.
Iight:
..... The 3rd line of defense in the immune system is Acquired Immunity which consists of specific defenses: lymphocytes (B cells and T cells) and antibodies(immunoglobulins).
This defense mechanism is activated in reponse to antigens on pathogens that are not recognized as self-cells or home-cells.
Antigens are proteins that serve as nametags for the t cells and b cells to recognize if a cell is a home cell or a foreigner.

B Cells mature in the bone marrow and belong to the humoral (body fluids) response system.
T cells mature in the thymus and belong to the cellular response system.
B Cells
There are two types of B cells: plasma cells and memory cells. The plasma cells produce anitbodies and make memory cells. The memory cells have a long term immunity to a specific antogen. They are the defense against attackers that are floating freely in the lymph and blood.

Antibodies: proteins that bind to specific antigens.
IgM: 1st immune response.
IgG: 2nd immune response: more antibodies in plasma
IgA: in external secretions
IgE: release of histamine, triggers allergic reactions
B cell immune response system.


The Helper T cell then releases interluekin 1 to produce more helper t cells to look for more infecter cells. It also releases interleukin 2 to alert the Killer T cells that there is an invader. This activates the Killer T Cells. The interleukin 2 also stimulates B cells to drop more anti bodies in case there are whole pathogens in the humoral system.
The killer t cells destroy the infected target cell by making holes in it (apoptosis). Since the membrane is now punctured the cell is no longer semi permeable it is wholy permeable and water rushes in from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution and the cell pops.

THATS ALL FOLKS
http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/immunity/index.html
Thursday, February 7, 2008

-clone
-release antibodies (proteins)
-memory cells = long term immunity

BREASTFEEDING (MATERNAL IMMUNITY)

-kerrie- p.s.- the sherpa for tom. will be saad
Tuesday, February 5, 2008
Immune/ Lymphatic system 1
There are many avenues of attack for foreign substances to enter your body.
- digestive system
- respiratory system
- urogenital tract
- break in the skin
Red and white blood cells are made from pluripotent stem cells in the bone marrow. These stem cells are then made into lymphoid stem cells and myeloid stem cells. The myeloid stem cells make red blood cells , basophils, eosinophils, neitrophils, monocytes, and platelets. Lymphoid stem cells make either B-Cells or T-Cells. B & T cells are the true immune system.
The first line of defense
Broad, external defense. such as walls and moats. this is the skin and mucous membranes. The skin includes external and external skin.
The physical and chemical defenses are non specific. The external barrier are epithelial cells and mucus membranes such . Examples are the skin, the respiratory system, the digestive system and the urogenital tract.
The chemical carriers on the epithelium are skin and mucous membrane secretions. Sweat, tears, mucus, saliva, stomach acid and anti-microbial proteins (such as lysozyme enzyme)
The Second Line of defense inclcludes internal, broad range patrol by many different cells and proteins such as mast cells, monocytes, macrophage and natural killer cells.
Leukocytes or phagocytic WBC's. Their attracted by a chemical signal released by damaged cells. Neutrophils are the most abundant and have a three day life span. Macrophages are "big eaters" and are long-lived. Natural killer cells destroy virus-infected cells and cancer cells.
In order to kill cells tho have gone bad , natural killer cells perforate cells, by releaseing perforin ( a protein) into the membrane of a target cell.. This forms a pore allowing fluid to flow into the cell. The cell then ruptures or lysis. This is call apoptosis. As Ms. Foglia says, its like "causing a cell to commit suicide"
Anti - microbial proteins awork as a complement system. 20 proteins circulating in blood plasma attack baterial and fungal cells. This forms a membrane attack complex which perforates target cells which also leads to apoptosis.
Inflammatory response is when damage to tissue triggers local non-specific inflammatory response. The cells then release histamines and prostaglandins. Capillaries then dilate and become more permeable This : increases blood supply, delivers WBC, RBC, Platelets & clotting factors. This accounts for swelling, redness and heat of inflammation & infection.
i cant get pictures because my computer is being difficult, i'm sorry this was boring, BUT tomorrow's sherpa will beeeeeeee...... KIM :)
GoodNight.
Monday, February 4, 2008
Muscle System
Smooth Muscle- Involuntary, Non-striated Muscle found in the digestive tract
Skeletal Muscle- Voluntary, Striated Muscle usually attatched to skeleton used to create movement
Cardiac Muscle- Involuntary, Striated auto-rhythmic, found in the heart
There are also three types of joints:
Ball and Socket Joints- Allow for 360 degree rotation example of this is the shoulder joint
Hinge joint- Allows for forward and backward motion such as that in your knee
Pivot Joint- allows for twisting motion such as that in your wrist or ankle
Muscles do work by contracting. When you flex your muscle the muscle shortens and thus enlargen in width. Skeletal muscles come in antagonist pairs flexor v. extensor: when flexing the bicep the bicep is contracting becoming the flexor and the tricep is stretched becoming the extensor. Tendons connect bone to muscle where ligaments connect bone to bone. Sarcomere is the unit responsible for muscle contraction, made up of thin and thick filaments Actin and Myosin. These interact at cross bridges between myosin heads and actin which are responsible for the shortening in muscles. The cleaving of atp to adp allows for myosin heads to bind to the actin filament. The shortening of the sarcomere allows for the contraction of the muscle when the (Z lines) move closer together.
The "Ratchet" System is due to the bonding of myosin with actin, then the sliding of thin and thick filaments past each other, then myosin head releases and binds to the active site on actin, and the muscle is unable to relax until Ca+2 is repumped into the sarcomeric reticulum. When all of this occurs the ratchet of the muscle occurs and muscles contract. For this to occur ATP is needed and greatly appreciated.

