- To make new cells
- Continuity of life: Asexual reproduction, growth, repair, and renewal
- Cell cycle: Make a copy of a preexisting cell (Daughter cells)
What's in a cell that smells so sweet.......ehhh

- Nucleus: Chromosomes, DNA
- Cytoskeleton: "Scaffolding" or "Skeleton"; The internal framework of a cell, composed largely of actin filaments and microtubules (spindle fibers). Also includes Centrioles (in animaks).
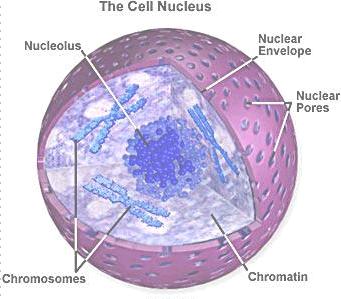
The Nucleus:
Its function: to protect DNA
Centrioles:
One of two cylindrical cellular structures that are composed of nine triplet microtubules and form the asters during mitosis.
Centrioles are involved in the organization of the mitotic spindle and in the completion of cytokinesis.
Centrioles are an important part of centrosomes, which are involved in organizing microtubules in the cytoplasm.
They organize spindle fibers and guide chromosmes in mitosis.
Daughter Cells:
During mitosis, an exact copy of DNA is made from the parent cell to be passed to the daughter cells.
Cytokinesis: division of orgnanelles and cytoplasm
Mitosis:
Interphase: Defined only by the absence of cell division. During interphase, the cell obtains nutrients, and duplicates its chromatids. Most eukaryotic cells spend approximately 90% of its life in Interphase. "Every day job": produces RNA, synthesize proteins and enzymes, prepares for duplication if triggered.
Prophase: Stage during which the chromosomes condense and become visible, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the spindle apparatus forms at opposite poles of the cell.
Pro-Metaphase: The stage of mitosis or meiosis in which the nuclear membrane disintegrates, the centrioles reach the poles of the cell, and the chromosomes continue to contract.
Metaphase: Condensed chromosomes align in the middle of the cell before being separated into each of the two daughter cells.
Anaphase: The chromosomes move from the equatorial plate toward opposite ends of the nuclear spindle.
Telophase: The chromosomes of daughter cells are grouped in new nuclei.
Cytokinesis: The division of the cytoplasm of a cell following the division of the nucleus.
Cell Life Cycle:
Interphase:
Divided into three phases:
-G1: first gap
Cell doing everyday job
Cell grows
-S: DNA Synthesis: Copies chromosomes
-G2: second gap
Prepares for division
Cell grows more
Produces organelles, proteins, and membranes
FIN
Oh tomorrows sherpa is...............Maria
2 comments:
Can you tell me which resolution power is best for the see chromosome in the microscope and details of techniques for chormosome slide preparation and staining.
you can mail me on my mail id chandpatel712in@gmail.com
Loved the vid. I think that it's really going to help me...
Post a Comment